The History of WordPress Security: Evolution and Best Practices
WordPress has grown from a humble blogging platform to powering over 43% of the web as of 2023. With its expansive reach comes an inevitable focus on security, making it a key concern for developers, administrators, and users alike. This article explores the history of WordPress security, highlighting its challenges, milestones, and evolution into the robust system it is today.
Table of Contents
- The Early Days of WordPress Security
- Growth and Vulnerabilities
- Major Security Milestones
- Current State of WordPress Security
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
The Early Days of WordPress Security
First Security Challenges
WordPress launched in 2003, and in its nascent stages, security wasn’t a top priority. The initial focus was on ease of use and functionality, leaving vulnerabilities in the core code and plugins. Early attacks often exploited insecure PHP code, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access or deface websites.
Common issues included:
- SQL Injection vulnerabilities due to improper sanitization of user inputs.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) exploits that allowed attackers to inject malicious scripts.
Community Response
In response to these challenges, the WordPress community rallied to address vulnerabilities. The WordPress Security Team, a dedicated group of core developers and volunteers, was established to monitor, identify, and patch security flaws.

Growth and Vulnerabilities
Plugin and Theme Security Risks
The rise of WordPress plugins and themes in the mid-2000s contributed significantly to its popularity. However, this also introduced substantial risks:
- Unvetted third-party contributions often contained vulnerabilities.
- Developers sometimes lacked security expertise, leading to exploitable flaws.
In 2011, over 30,000 websites were compromised due to vulnerabilities in outdated plugins like TimThumb.
High-Profile Exploits
Some major security incidents that highlighted WordPress’s vulnerabilities included:
- 2014 XML-RPC Pingback Attack: Exploited to launch large-scale DDoS attacks.
- 2018 GDPR Plugin Vulnerability: An XSS flaw affecting sites implementing GDPR compliance plugins.
These incidents showcased the importance of proactive measures and ongoing vigilance.
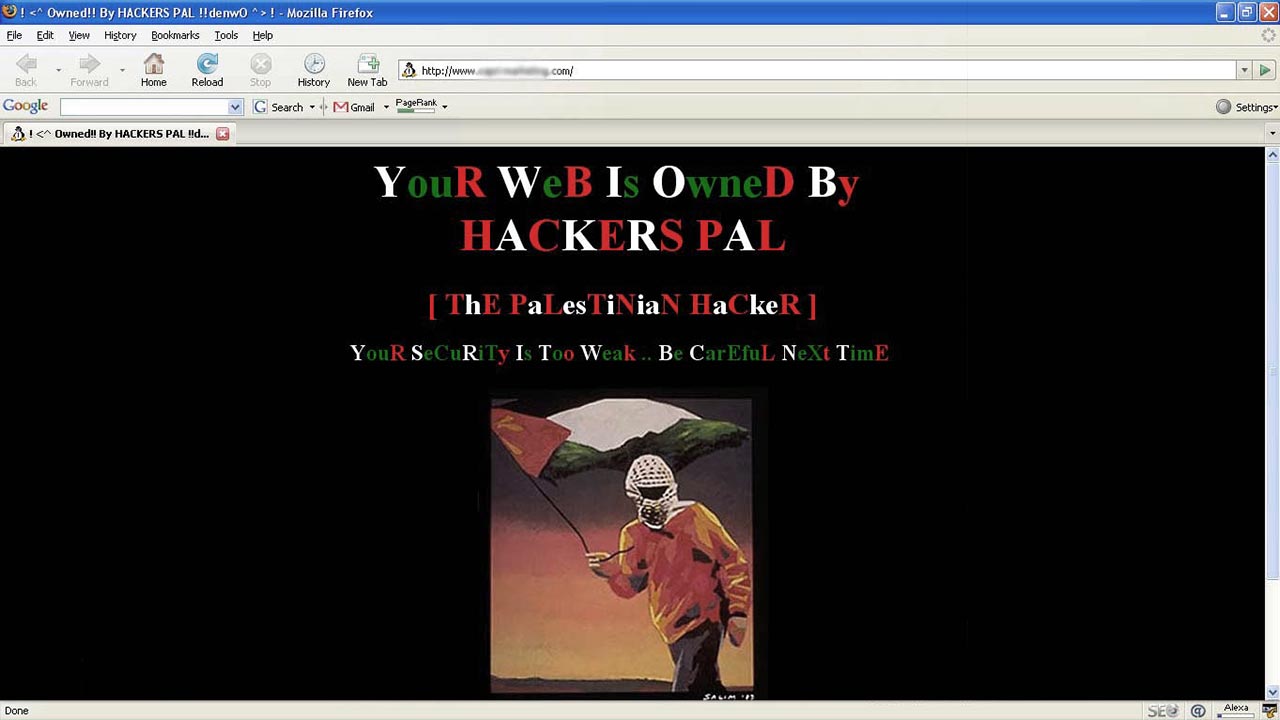
Image of a hacked WordPress website, happened around 2003-04
Major Security Milestones
Introduction of Automatic Updates
In 2013, WordPress introduced automatic background updates for minor releases (starting with version 3.7). This step was pivotal in ensuring users received critical security patches without manual intervention.
Two-Factor Authentication
As brute-force attacks became more common, WordPress began supporting two-factor authentication (2FA) through plugins like Wordfence and iThemes Security. This added a crucial layer of protection for user accounts.
Integration with Security Plugins
The emergence of robust security plugins like Wordfence, Sucuri, and All In One WP Security transformed how users approached WordPress security. These tools provided features such as:
- Malware scanning
- Firewall protection
- Login attempt monitoring

Current State of WordPress Security
WordPress Core Improvements
The WordPress Security Team continues to refine the core, prioritizing:
- Code sanitization and validation to prevent SQL injection and XSS attacks.
- Strict policies on plugins and themes listed in the WordPress repository.
Modern Threats and Challenges
Today, WordPress faces sophisticated threats, including:
- Zero-Day Vulnerabilities: Exploited before patches are available.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting third-party plugins and libraries.
Efforts to mitigate these include regular security audits, threat intelligence sharing, and tighter integration with hosting providers for managed security services.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
The evolution of WordPress security is a testament to the platform’s commitment to protecting its users. From its early days of reactive fixes to the proactive measures we see today, WordPress has come a long way. The most important takeaway is that security is a shared responsibility—users, developers, and hosting providers must collaborate to maintain a safe web environment.
Resources
- WordPress Security Team
- Sucuri: WordPress Security Guide
- Wordfence Blog
- Official WordPress Developer Handbook
- iThemes Security






Leave A Comment