The History of Amiga MODs: Revolutionizing Digital Music
The Amiga MOD (Module) format transformed the music landscape in the late 1980s and early 1990s, merging innovative technology with creative artistry. This article explores the history, evolution, and lasting impact of Amiga MODs on the digital music and computing worlds.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Amiga MODs
- Origins and Development
- Technological Innovation
- The MOD Scene
- Legacy and Modern Influence
- Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- Final Thoughts
- Resources
Introduction to Amiga MODs
The Amiga MOD format symbolizes a defining moment in the digital audio revolution, offering musicians the ability to create multi-channel compositions on a personal computer.
What is a MOD File?
A MOD file is a music file format that originated on the Commodore Amiga in the late 1980s. Unlike MIDI, which relies on synthesizers to generate sounds, MOD files include digitized audio samples and playback instructions, allowing for rich, portable soundtracks.
The Role of the Amiga Computer
Commodore’s Amiga line, particularly the Amiga 500, featured advanced multimedia capabilities that made it a favorite for creative projects. The computer’s powerful sound chip and processing ability made MOD music possible, democratizing music production for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Origins and Development
It all started with the SID
The SID (Sound Interface Device) is a legendary audio chip developed by MOS Technology for the Commodore 64 (C64) and Commodore 128 computers. Introduced in 1982, the SID revolutionized computer sound by delivering rich, complex audio capabilities previously unheard of in consumer-grade machines. Designed by Bob Yannes, the chip featured three independent oscillators, a versatile waveform generator, and an analog filter, enabling it to produce dynamic music and sound effects. Its distinct sound has influenced generations of musicians and is a cornerstone of the chiptune music genre.
The Birth of the MOD Format
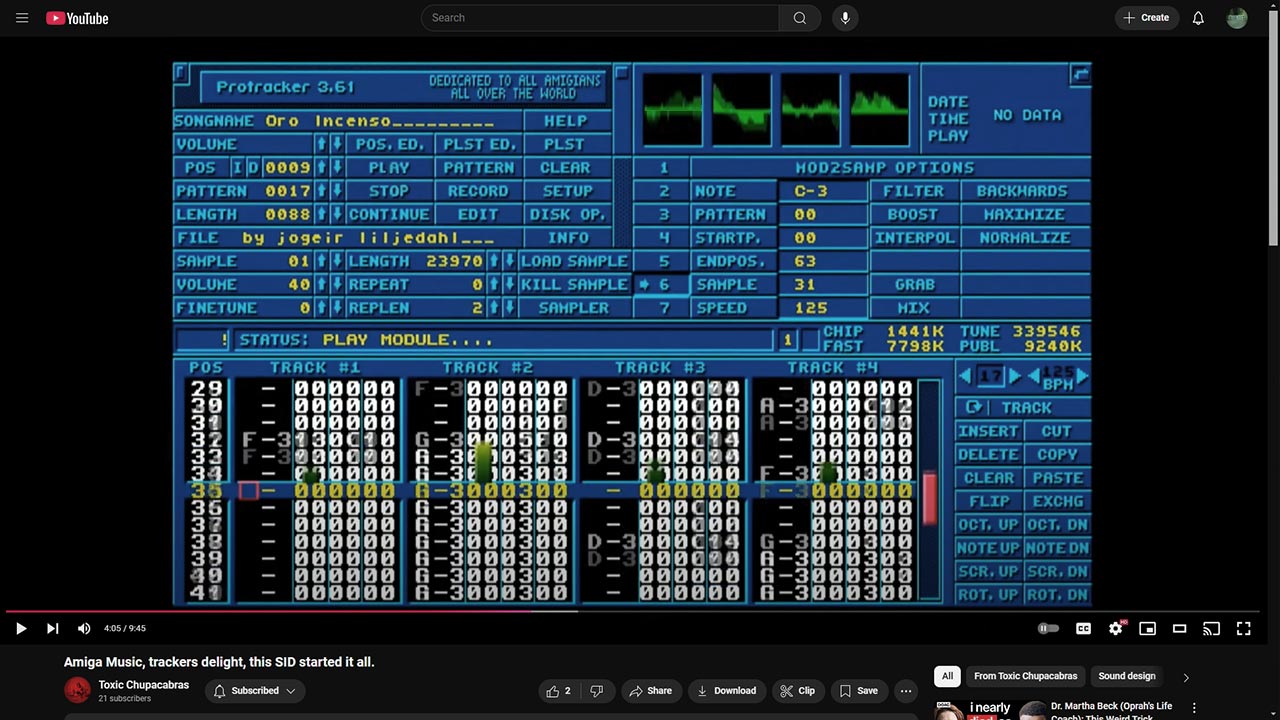
The MOD format was introduced in 1987 by Karsten Obarski, the developer of Ultimate Soundtracker, the first tracker software for the Amiga. It allowed users to arrange audio samples on multiple tracks, essentially pioneering modern digital music sequencing.
Pioneering Creators and Tools
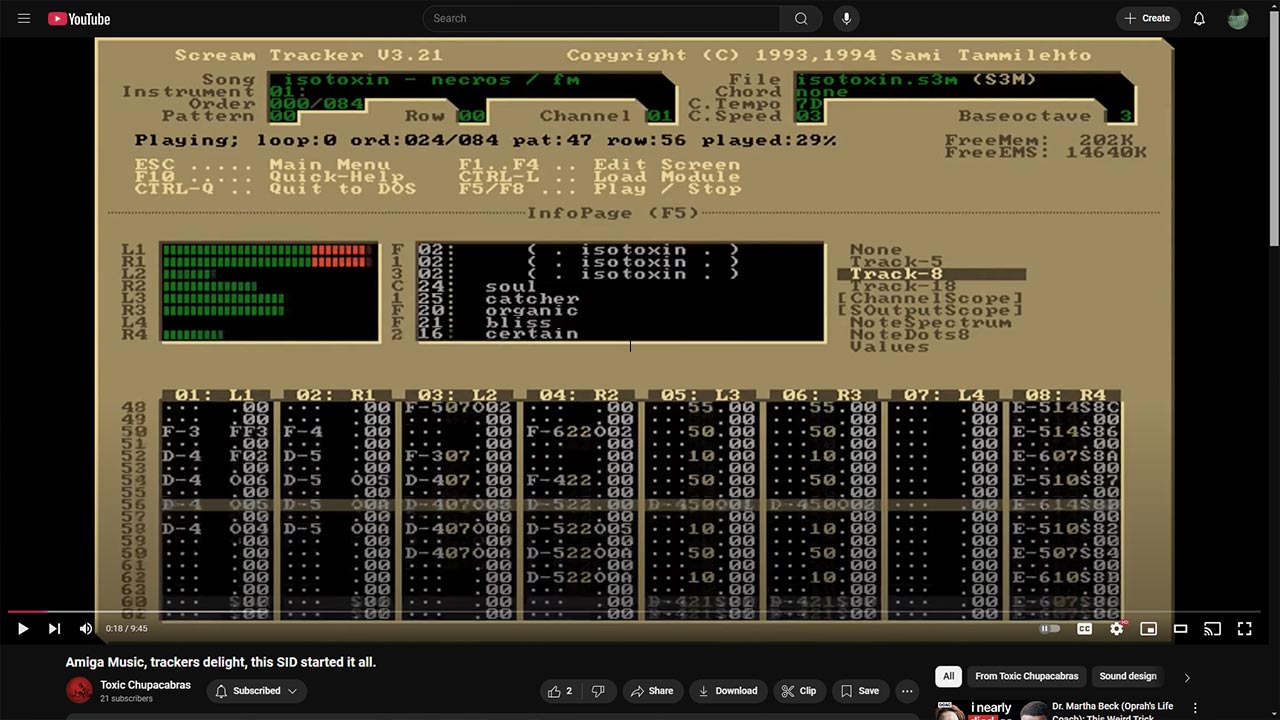
Following Obarski’s groundbreaking work, enthusiasts created tools like ProTracker, ScreamTracker, NoiseTracker, and OctaMED, each pushing the limits of what could be done with MOD music. These tools empowered users to compose complex pieces despite limited computing power.
Technological Innovation
How MODs Worked
A MOD file consists of:
- Samples: Digitized sound snippets for playback.
- Patterns: Grids of notes and effects for each track.
- Track Data: Instructions for sequencing patterns.
This format supported up to four audio channels on early Amiga models, expanded later with software optimizations.
Impact of Paula Sound Chip
The Paula sound chip, a core component of the Amiga, provided 8-bit stereo audio output. It could handle direct memory access (DMA) operations, making real-time playback of MOD files efficient and seamless.
The MOD Scene
MODs and Demoscene Culture
The Demoscene, a subculture focused on creating artistic demos showcasing computer capabilities, embraced MOD music. MODs added an immersive auditory element to visuals, making demos unforgettable.
Rise of MOD Composers
Talented composers like Jesper Kyd, Jeroen Tel, and Allister Brimble gained fame within the MOD and video game communities. Their works showcased MOD’s potential for emotional depth and technical brilliance.
Legacy and Modern Influence
The MOD Renaissance
Though eclipsed by newer formats in the late 1990s, MOD music saw a resurgence with the advent of MOD emulators and trackers for modern platforms. Open-source projects like OpenMPT and MilkyTracker keep the format alive.
MODs in Contemporary Media
MOD music remains influential in retro gaming, indie game development, and chiptune music scenes. Its legacy is evident in genres where resource efficiency and creativity intersect.
Top 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Final Thoughts
The Amiga MOD format represents a milestone in digital music history, blending technology and creativity in unprecedented ways. Its influence is felt far beyond the demoscene and retro gaming, shaping how we approach music composition, distribution, and multimedia integration. Today, MODs remain a testament to the enduring power of ingenuity and community.
Resources
- Amiga History Saga
- OpenMPT Tracker
- The MOD Archive
- MilkyTracker
- “A History of the Amiga MOD Scene” – Retro Computing Magazine, 2023.





Leave A Comment